The Land of Two Promises – the Complete History of Israel-Palestine conflict
The Israel-Palestine conflict is a complex and long-standing conflict between the State of Israel and the Palestinian people. The conflict has its roots in the early 20th century, when European Jews began to immigrate to Ottoman Palestine. The Ottoman Empire collapsed after World War I, and the British Mandate for Palestine was established. The British Mandate was intended to facilitate the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine, but it also led to tensions between the Jewish and Arab populations.
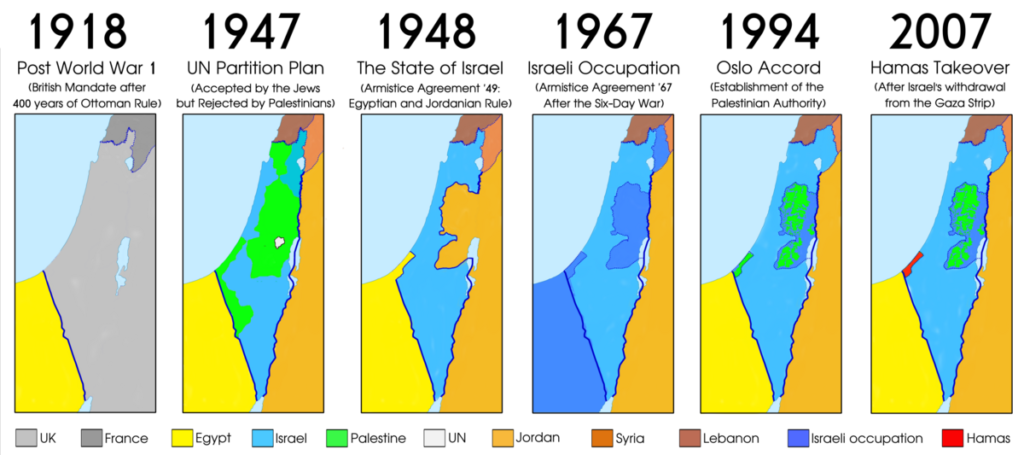
In 1947, the United Nations proposed the Partition Plan for Palestine, which would have divided Palestine into two states, one Jewish and one Arab. The Arab League rejected the Partition Plan, and the British Mandate ended in 1948. Israel declared its independence on May 14, 1948, and the following day, the Arab-Israeli War broke out. The war ended with Israel controlling most of former British Mandate Palestine.
Since 1948, there have been several wars and numerous smaller conflicts between Israel and the Palestinians. The conflict has also been marked by violence and terrorism. In recent years, there has been a growing movement for a two-state solution to the conflict, but there is no agreement on the borders of the two states or on other key issues.
The Israel-Palestine conflict is a complex and intractable conflict with no easy solutions. The conflict has had a devastating impact on both Israelis and Palestinians, and it has also had a significant impact on the Middle East region and the world.
Here is a more detailed timeline of some of the key events in the Israel-Palestine conflict:
- 1880s: European Jews begin to immigrate to Ottoman Palestine.
- 1917: The Balfour Declaration is issued, which states that the British government favors the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
- 1922: The League of Nations establishes the British Mandate for Palestine.
- 1947: The United Nations proposes the Partition Plan for Palestine.
- 1948: Israel declares its independence and the Arab-Israeli War breaks out.
- 1967: The Six-Day War results in Israel capturing the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and East Jerusalem.
- 1973: The Yom Kippur War is fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states.
- 1978: The Camp David Accords are signed between Israel and Egypt.
- 1993: The Oslo Accords are signed between Israel and the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO).
- 2000: The Second Intifada begins.
- 2005: Israel withdraws from Gaza.
- 2008: The Gaza War is fought between Israel and Hamas.
- 2012: The Gaza War is fought between Israel and Hamas.
- 2014: The Gaza War is fought between Israel and Hamas.
- 2022: The Israel-Palestine conflict continues, with no end in sight.
- 2023: Israel-Palestine conflict: Ongoing and volatile, with risk of further escalation
The Israel-Palestine conflict is a complex and tragic conflict with no easy solutions. It is important to understand the history of the conflict in order to understand the present and to work towards a peaceful resolution.
The History and Identity of the Jewish People
The history of the Jewish people is a long and rich one, dating back over 3,500 years. The Jews are a monotheistic people who believe in one God, and their religion is Judaism. Judaism is one of the oldest religions in the world, and it has had a profound impact on Western civilization.
The history of the Jewish people can be divided into two main periods: the biblical period and the post-biblical period. The biblical period begins with the creation of the world and ends with the destruction of the First Temple in Jerusalem in 586 BCE. During this period, the Jews developed their religious beliefs and traditions.
The post-biblical period begins with the return of the Jews to Jerusalem in 538 BCE and continues to the present day. During this period, the Jews have faced many challenges, including persecution and exile. However, they have also made significant contributions to society in many areas, including science, medicine, and the arts.
Here is a more detailed timeline of some of the key events in the history of the Jewish people:
- 1200 BCE: The Israelites arrive in Canaan, the land that God promised to Abraham.
- 1000 BCE: King David establishes the united kingdom of Israel.
- 960 BCE: Solomon builds the First Temple in Jerusalem.
- 586 BCE: The Babylonians destroy the First Temple and exile the Jews.
- 538 BCE: The Persians conquer Babylon and allow the Jews to return to Jerusalem.
- 165 BCE: The Maccabees defeat the Greeks and establish the Hasmonean dynasty.
- 63 BCE: The Romans conquer Judea and establish the Roman province of Judea.
- 70 CE: The Romans destroy the Second Temple in Jerusalem.
- 132 CE: The Bar Kokhba revolt is crushed by the Romans.
- 425 CE: The Council of Chalcedon excludes the Jews from Christianity.
- 1096 CE: The First Crusade begins with the massacre of Jews in Europe.
- 1492 CE: The Spanish Inquisition forces Jews to convert to Christianity or leave Spain.
- 1948 CE: The State of Israel is established.
- 1967 CE: The Six-Day War results in Israel capturing the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and East Jerusalem.
The history of the Jewish people is a complex and fascinating one. The Jews have faced many challenges throughout their history, but they have also made significant contributions to society. The Jewish people are a resilient people, and they continue to thrive today.
The key events in the Israel-Palestine in Detail:
1880s: European Jews begin to immigrate to Ottoman Palestine.
In the 1880s, European Jews began to immigrate to Ottoman Palestine in significant numbers. This was due to a number of factors, including:
- Persecution in Europe: Jews faced widespread persecution and discrimination in Europe, including pogroms and anti-Jewish laws.
- The Zionist movement: The Zionist movement, which advocated for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine, was gaining momentum.
- Economic opportunities: Palestine was seen as a land of economic opportunity, with its fertile soil and warm climate.
The first wave of Jewish immigration to Palestine was led by religious Zionists, who believed that it was their religious duty to return to the Promised Land. These immigrants established agricultural settlements and religious schools.
In the early 1900s, a second wave of Jewish immigration began, led by secular Zionists. These immigrants were motivated by a desire to create a Jewish homeland and to escape the anti-Semitism they faced in Europe. The second wave of immigrants established cities and industries, and they transformed Palestine into a more cosmopolitan and modern society.
The immigration of European Jews to Ottoman Palestine had a profound impact on the region. It led to increased tensions between the Jewish and Arab populations, and it ultimately contributed to the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948.
1917: The Balfour Declaration is issued, which states that the British government favors the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
The Balfour Declaration was a letter from British Foreign Secretary Arthur Balfour to Lionel Walter Rothschild, a leader of the British Zionist movement. The letter was issued on November 2, 1917, and it stated that the British government favored the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
The Balfour Declaration was a significant event in the history of the Zionist movement. It was the first time that a major power had publicly expressed support for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine. The declaration also gave international legitimacy to the Zionist movement.
The Balfour Declaration was controversial from the start. The Arab population of Palestine opposed the declaration, as they feared that it would lead to the establishment of a Jewish state in Palestine. The Arab League rejected the declaration, and it has remained a source of tension between the Israelis and the Palestinians ever since.
Despite the controversy, the Balfour Declaration had a profound impact on the course of history. It helped to pave the way for the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948. The declaration also continues to be a source of debate and controversy today.
1922: The League of Nations establishes the British Mandate for Palestine.
The British Mandate for Palestine was a League of Nations Mandate that was established in 1922. The mandate gave Britain the responsibility of administering Palestine until it was ready for independence. The mandate also included a provision for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
The British Mandate for Palestine was a complex and controversial period in Palestinian history. The British government struggled to balance the interests of the Jewish and Arab populations, and there was frequent violence and unrest. The mandate also coincided with the rise of Zionism, the movement for the establishment of a Jewish state in Palestine.
The British Mandate for Palestine ended in 1948 with the establishment of the State of Israel. The Arab-Israeli War broke out shortly after Israel’s independence, and the war resulted in the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians.
1947: The United Nations proposes the Partition Plan for Palestine.
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations, which recommended a partition of Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. On 29 November 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted the Plan as Resolution 181 (II).
The Partition Plan proposed to divide Palestine into two states, one Arab and one Jewish, with Jerusalem placed under a special international regime. The Arab state would have been allocated 55% of the territory, while the Jewish state would have been allocated 45% of the territory. Jerusalem would have been under the administration of the United Nations Trusteeship Council for ten years, after which a referendum would have been held to determine its permanent status.
The Partition Plan was accepted by the Jewish Agency for Palestine, but it was rejected by the Arab League and the Palestinian Arab leadership. The Arab League declared that it would invade Palestine if the Partition Plan was implemented.
The Partition Plan was never fully implemented. On 14 May 1948, the British Mandate for Palestine ended, and the State of Israel declared its independence. The following day, the Arab League invaded Palestine, and the 1948 Arab-Israeli War broke out.
The war resulted in the defeat of the Arab armies and the establishment of the State of Israel. The war also resulted in the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians.
1948: Israel declares its independence and the Arab-Israeli War breaks out.
On May 14, 1948, the State of Israel declared its independence. The following day, the Arab League invaded Palestine, and the 1948 Arab-Israeli War broke out.
The war lasted for 10 months and resulted in the defeat of the Arab armies. Israel gained control of much of the territory that had been allocated to the Arab state in the UN Partition Plan. Hundreds of thousands of Palestinians were displaced from their homes during the war.
The 1948 Arab-Israeli War was a watershed moment in the history of the conflict. It established Israel as a sovereign state and led to the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians. The war also set the stage for the many years of conflict and violence that have followed.
The 1948 Arab-Israeli War is a complex and controversial event. There are many different perspectives on the war and its causes. However, there is no doubt that the war had a profound impact on the course of history.
The war also had a significant impact on the Palestinian people. The displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians during the war led to the creation of the Palestinian refugee problem. The refugee problem remains a major obstacle to peace between Israel and the Palestinians today.
The 1948 Arab-Israeli War was a tragic event that had a profound impact on the region. It is important to remember the war and its victims, and to work towards a just and lasting peace.
1967: The Six-Day War results in Israel capturing the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and East Jerusalem.
The Six-Day War was a war fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states from June 5 to June 10, 1967. The war resulted in Israel capturing the West Bank, Gaza Strip, East Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights.
The war began with a surprise attack by Israel on Egypt. Israel quickly defeated the Egyptian air force and captured the Sinai Peninsula. Israel then attacked Jordan and captured the West Bank and East Jerusalem. Finally, Israel attacked Syria and captured the Golan Heights.
The Six-Day War was a decisive victory for Israel. Israel gained control of a large amount of territory that had been previously controlled by Arab states. The war also led to a significant increase in the number of Palestinians under Israeli control.
The Six-Day War had a profound impact on the Arab-Israeli conflict. It led to a hardening of positions on both sides of the conflict. The Arab states were determined to liberate the territories that they had lost to Israel. Israel was determined to maintain control of the territories that it had captured.
The Six-Day War also led to a surge in international support for the Palestinian cause. The international community condemned Israel’s occupation of the West Bank and Gaza Strip. The United Nations Security Council passed Resolution 242, which called for the withdrawal of Israeli forces from the territories that they had captured in the war.
The Six-Day War was a turning point in the Arab-Israeli conflict. It led to a new era of violence and tension in the region. The war also made it more difficult to achieve a lasting peace.
The Six-Day War was a complex and controversial event. There are many different perspectives on the war and its causes. However, there is no doubt that the war had a profound impact on the course of history.
The war had a significant impact on the Palestinian people. The occupation of the West Bank and Gaza Strip has had a devastating impact on the lives of Palestinians. The occupation has also made it difficult for Palestinians to achieve self-determination.
The Six-Day War was a tragic event that had a profound impact on the region. It is important to remember the war and its victims, and to work towards a just and lasting peace.
1973: The Yom Kippur War is fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states.
The Yom Kippur War was a war fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states from October 6 to October 25, 1973. The war began with a surprise attack by Egypt and Syria on Israel on the holiest day of the Jewish calendar, Yom Kippur.
The Arab armies achieved initial success, and Israel was caught off guard. However, Israel was able to mobilize its forces and eventually turn the tide of the war. Israel pushed back the Arab armies and regained control of most of the territory that had been lost in the initial attack.
The Yom Kippur War was a costly war for both sides. Over 20,000 people were killed, and thousands more were wounded. The war also had a significant economic impact on both sides.
The Yom Kippur War had a profound impact on the Arab-Israeli conflict. It led to a renewed sense of urgency on both sides to achieve a lasting peace. The war also led to a number of diplomatic initiatives, including the Camp David Accords and the Oslo Accords.
The Yom Kippur War was a complex and controversial event. There are many different perspectives on the war and its causes. However, there is no doubt that the war had a profound impact on the course of history.
The war had a significant impact on the Palestinian people. The war led to a renewed sense of Palestinian nationalism and a desire for self-determination. The war also led to an increase in international support for the Palestinian cause.
The Yom Kippur War was a tragic event that had a profound impact on the region. It is important to remember the war and its victims, and to work towards a just and lasting peace.
1978: The Camp David Accords are signed between Israel and Egypt.
The Camp David Accords were signed between Israel and Egypt on September 17, 1978. The accords were the result of negotiations between Egyptian President Anwar Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin. The accords were mediated by US President Jimmy Carter.
The Camp David Accords called for a peace treaty between Israel and Egypt, the withdrawal of Israeli forces from the Sinai Peninsula, and the establishment of a self-governing authority for the Palestinians in the West Bank and Gaza Strip.
The Camp David Accords were a major breakthrough in the Arab-Israeli conflict. They were the first peace treaty between Israel and an Arab country. The accords also paved the way for the establishment of the Palestinian Authority in 1994.
The Camp David Accords were not without their critics. Some Palestinians argued that the accords did not go far enough in addressing Palestinian grievances. Others argued that the accords were a betrayal of the Palestinian cause.
Despite the criticism, the Camp David Accords were a significant achievement. They helped to reduce tensions in the Middle East and created a new atmosphere of cooperation between Israel and Egypt.
The Camp David Accords were a complex and controversial event. However, there is no doubt that they had a profound impact on the course of history. The accords helped to pave the way for a more peaceful future in the Middle East.
1993: The Oslo Accords are signed between Israel and the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO).
The Oslo Accords were signed between Israel and the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) on September 13, 1993. The accords were the result of secret negotiations between Israeli Foreign Minister Shimon Peres and PLO Chairman Yasser Arafat. The accords were mediated by Norwegian Foreign Minister Johan Jørgen Holst.
The Oslo Accords called for a phased withdrawal of Israeli forces from the West Bank and Gaza Strip, the establishment of a Palestinian Authority in the West Bank and Gaza Strip, and the negotiation of a final status agreement between Israel and the Palestinians.
The Oslo Accords were a major breakthrough in the Arab-Israeli conflict. They were the first direct negotiations between Israel and the PLO. The accords also created a new framework for resolving the conflict.
The Oslo Accords were not without their challenges. They were met with opposition from both Israelis and Palestinians. However, the accords also generated a great deal of hope for peace.
The Oslo Accords helped to reduce tensions in the Middle East and created a new atmosphere of cooperation between Israel and the Palestinians. However, the accords have not yet been fully implemented. The final status agreement has not been negotiated, and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains unresolved.
Despite the challenges, the Oslo Accords remain an important milestone in the history of the Arab-Israeli conflict. They represent a commitment to peace and a recognition of the need for a two-state solution to the conflict.
2000: The Second Intifada begins.
The Second Intifada began on September 28, 2000, after Ariel Sharon, then the leader of the Likud Party, visited the Temple Mount in Jerusalem. The visit was seen by many Palestinians as a provocation and led to widespread protests and violence.
The Second Intifada was a much more violent uprising than the First Intifada. It was characterized by suicide bombings, targeted killings, and rocket attacks. The conflict also had a significant impact on the Israeli economy and society.
The Second Intifada lasted for over five years and resulted in the deaths of over 3,000 Palestinians and over 1,000 Israelis. The conflict also led to the destruction of property and infrastructure on both sides.
The Second Intifada was a major setback for the peace process. It eroded trust between the Israelis and Palestinians and made it more difficult to reach a comprehensive peace agreement.
The Second Intifada was a complex and controversial event. There are many different perspectives on the conflict and its causes. However, there is no doubt that the conflict had a profound impact on the course of history.
The Second Intifada had a significant impact on the Palestinian people. The conflict caused widespread death and destruction, and it made it difficult for Palestinians to rebuild their lives. The conflict also led to a decline in the Palestinian economy and a rise in poverty and unemployment.
The Second Intifada was a tragic event that had a profound impact on the region. It is important to remember the conflict and its victims, and to work towards a just and lasting peace.
2005: Israel withdraws from Gaza.
Israel’s disengagement from Gaza was a unilateral withdrawal of Israeli troops and settlers from the Gaza Strip in 2005. The withdrawal was carried out by the government of Ariel Sharon, who argued that it was necessary to end the Second Intifada and to create a more secure environment for Israelis.
The disengagement from Gaza was a controversial decision. It was opposed by many Israelis, who argued that it would endanger Israel’s security and would lead to the rise of Hamas in Gaza. The disengagement was also opposed by many Palestinians, who argued that it did not go far enough and that it did not address the core issues of the conflict.
Despite the opposition, the disengagement from Gaza was carried out. The withdrawal of Israeli troops and settlers was completed in August 2005.
The disengagement from Gaza was a symbolic step towards peace. It was the first time that Israel had withdrawn from territory that it had conquered in the 1967 Six-Day War. The withdrawal also showed that Israel was willing to take unilateral steps to improve the security situation.
The disengagement from Gaza did not lead to an end to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. However, it did create a new opportunity for peace. The Palestinians now have control over their own territory in Gaza, and they have the opportunity to build a state. The Israelis have also reduced their military presence in the Gaza Strip, which has created a more peaceful environment.
The disengagement from Gaza was a complex and controversial event. However, it is important to remember that it was a step towards peace. The withdrawal of Israeli troops and settlers from Gaza created a new opportunity for the Israelis and Palestinians to resolve their conflict.
2008: The Gaza War is fought between Israel and Hamas.
The Gaza War was a military conflict fought between Israel and Hamas from December 27, 2008, to January 18, 2009. The war was initiated by Israel with the stated aim of halting rocket fire from Gaza into Israel and of destroying Hamas’s military capabilities.
The Gaza War was a major escalation in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. It was the deadliest conflict between Israel and Hamas since the Second Intifada. The war resulted in the deaths of over 1,400 Palestinians and over 13 Israelis. The war also led to widespread destruction of property and infrastructure in Gaza.
The Gaza War was a major setback for the peace process. It eroded trust between the Israelis and Palestinians and made it more difficult to reach a comprehensive peace agreement.
The Gaza War was a complex and controversial event. There are many different perspectives on the conflict and its causes. However, there is no doubt that the conflict had a profound impact on the course of history.
The Gaza War had a significant impact on the Palestinian people. The conflict caused widespread death and destruction, and it made it difficult for Palestinians to rebuild their lives. The conflict also led to a decline in the Palestinian economy and a rise in poverty and unemployment.
The Gaza War was a tragic event that had a profound impact on the region. It is important to remember the conflict and its victims, and to work towards a just and lasting peace.
2012: The Gaza War is fought between Israel and Hamas.
The Gaza War of 2012, also known as Operation Pillar of Defense, was a military conflict between Israel and Palestinian militant groups, primarily Hamas, in the Gaza Strip that lasted from November 14 to November 21, 2012. The conflict resulted in numerous casualties and significant damage to infrastructure in both Gaza and southern Israel.
The immediate trigger for the conflict was the escalation of hostilities between Israel and Hamas, which had been exacerbated by increased rocket attacks from Gaza into southern Israel and Israeli airstrikes targeting militants in the Gaza Strip. The Israeli government initiated Operation Pillar of Defense with the aim of halting the rocket attacks and diminishing the capabilities of Hamas and other militant groups.
During the conflict, both sides suffered casualties, with numerous civilian deaths and injuries reported in Gaza and a smaller number in Israel. The conflict ended with an Egypt-brokered ceasefire agreement, which included provisions for the cessation of hostilities and the easing of restrictions on the movement of people and goods in and out of the Gaza Strip.
The 2012 Gaza War was one of several conflicts between Israel and Hamas, and it further exacerbated the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict, leading to discussions about the broader issues affecting the region and the potential for a lasting peace agreement.
2014: The Gaza War is fought between Israel and Hamas.
The Gaza War of 2014, also known as Operation Protective Edge, was a military conflict between Israel and Hamas, the militant group that controls the Gaza Strip. The conflict began on July 8, 2014, following a significant escalation of tensions between the two sides, with Hamas launching rocket attacks into Israel and Israel conducting airstrikes and a ground invasion of the Gaza Strip in response.
The war resulted in significant casualties and destruction in the Gaza Strip, with numerous civilian deaths and injuries reported, as well as damage to infrastructure and residential areas. Israel’s Iron Dome missile defense system intercepted many of the rockets fired from Gaza, while Israel carried out airstrikes and a ground incursion to target Hamas militants and destroy their infrastructure.
International efforts were made to broker a ceasefire, with several temporary ceasefires implemented during the conflict. Ultimately, a ceasefire agreement was reached on August 26, 2014, which led to a cessation of hostilities and the easing of restrictions on the movement of goods and people in and out of the Gaza Strip.
The 2014 Gaza War further complicated the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and highlighted the challenges of achieving a lasting peace agreement in the region. The conflict drew significant international attention and criticism, with concerns raised about the humanitarian situation in Gaza and the long-term prospects for stability and peace in the region.
2022: The Israel-Palestine conflict continues, with no end in sight.
The Israel-Palestine conflict is a protracted armed conflict that began in the late 19th century with the rise of Zionism and the Jewish nationalist movement, and the competing Palestinian nationalist movement. The conflict is deeply rooted in nationalism, religion, and territorial claims.
In 2022, the conflict continued, with no end in sight. There were several major developments in the conflict, including:
- An 11-day war in Gaza in May 2022. The war began after Hamas, the Islamist militant group that controls Gaza, fired rockets at Israel in retaliation for Israeli police raids on the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound in Jerusalem. The Israeli military responded with airstrikes on Gaza, and Hamas and other Palestinian armed groups continued to fire rockets at Israel. The war ended with a ceasefire, but the underlying causes of the conflict remain unresolved.
- Continued Israeli settlement activity in the West Bank. Israeli settlements in the West Bank are considered illegal under international law, but Israel continues to build and expand them. Settlements have been a major obstacle to peace negotiations, as they make it difficult to create a two-state solution to the conflict.
- Increased violence between Israelis and Palestinians. In 2022, there was a significant increase in violence between Israelis and Palestinians, both in the West Bank and in Israel itself. This violence has included shootings, stabbings, and other attacks.
The international community has been unable to resolve the Israel-Palestine conflict. The United Nations has passed numerous resolutions on the conflict, but they have not been implemented. The United States has also tried to mediate a peace agreement between the two sides, but these efforts have been unsuccessful.
The Israel-Palestine conflict is a complex and difficult one, and there is no easy solution. However, it is important to continue to work towards a peaceful resolution of the conflict. The people of Israel and Palestine deserve to live in peace and security.
2023: Israel-Palestine conflict: Ongoing and volatile, with risk of further escalation
The Israel-Palestine conflict is ongoing as of November 3, 2023. In October 2023, Hamas launched a surprise attack on Israel, killing and wounding dozens of people. Israel responded with airstrikes on Gaza, killing hundreds of Palestinians. The conflict has since escalated, with both sides exchanging rocket fire and airstrikes.
The current situation is very fluid, and it is difficult to say with certainty what will happen next. However, there are a few key developments to watch:
- Israel has not yet launched a ground invasion of Gaza. This is a significant development, as it suggests that Israel is trying to avoid a wider conflict. However, it is still possible that Israel could launch a ground invasion if the situation deteriorates further.
- Hamas has not yet used long-range rockets to target major Israeli cities. This is also a significant development, as it suggests that Hamas is trying to avoid provoking a wider Israeli response. However, it is still possible that Hamas could use long-range rockets if the conflict escalates further.
- There is growing international pressure on both sides to de-escalate. The United Nations, the United States, and other countries have called on both sides to halt fire and return to talks. However, it is unclear whether either side is willing to do so at this time.
Overall, the situation in Israel and Palestine is very serious and there is a risk of further escalation. It is important to monitor the situation closely and to be prepared for further developments.
Here are some specific concerns:
- The humanitarian situation in Gaza is deteriorating rapidly. There is a shortage of food, water, and medical supplies.
- The conflict could spread to the West Bank, which could lead to a wider and more protracted conflict.
- The conflict could also destabilize the region, leading to increased tensions between Israel and its neighbors.
It is important to remember that the Israel-Palestine conflict is a complex and long-standing one. There is no easy solution, and it is likely to continue for many years to come.
At present, Hamas is designated as a terrorist organization by several countries and international entities, including the United States, the European Union, Israel, Canada, and Japan.