CELL AND CELLULAR ORGANIZATION
Summary of cell and cellular organization
Solved exercise of cell and cellular organization

Summary
Our planet earth, there are numerous varieties of plants and animals living in different habitats including there are also a variety of organisms like viruses, bacteria, lower forms of plants and animals. These organisms are not visible to the naked eye but are visible under a microscope. Hence, such organisms are called micro-organisms. Microscope: Used to see the objects which cannot be seen through our naked eyes.
What is the body of these Organisms made up of ?

Cell: A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of an organism. Cells were discovered by Robert Hooke an English scientist who discovered the cells. He viewed a thin slice of cork through a microscope, he was amazed to see tiny compartments closely arranged like a honeycomb. He named these tiny structures as cells.
Cell made up of?
A cell is made up of a colorless jelly-like substance called protoplasm. It is enclosed by a membrane called the cell membrane or plasma membrane. Each cell contains a nucleus and cytoplasm, nucleoplasm which is surrounded by a nuclear membrane. The Protoplasm present between the nucleus and the plasma membrane is known as cytoplasm. cytoplasm, there are several tiny structures called cell organelles.
Protoplasm

The Protoplasm present between the nucleus and the plasma membrane is known as Cytoplasm. Inside the cytoplasm there are several tiny structures called cell organelles. Organelle Living component in a cell with specific structure and function.
Are the cells of all organisms Similar.
Yes. The basic structure of cells of different organisms is similar.
There are two basic types of cells based on their structure. They are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic
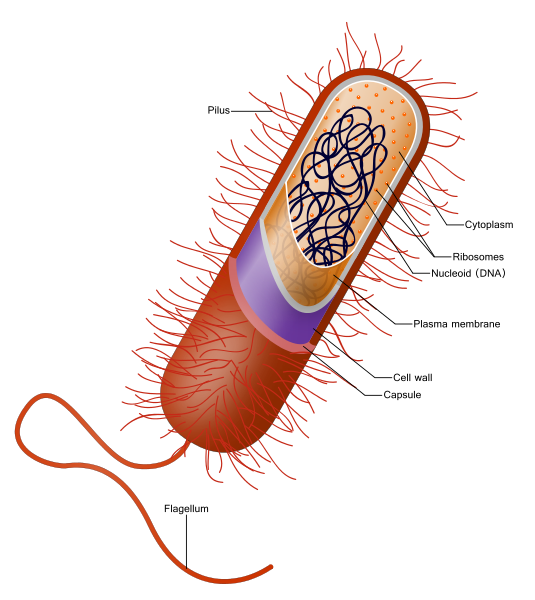
The cytoplasm shows small ribosomes but organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi complex are absent A cell with this pattern of the structure is called a prokaryotic cell, and the organism that possesses this type of a cell is called a prokaryote. Prokaryotic cells are seen in bacteria, cyanobacteria, and mycoplasmas.
Eukaryotic cells

Cytoplasm shows large ribosomes and organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi complex. A cell with this pattern of the structure is called a eukaryotic cell and the organism that possesses this type of cell is called a eukaryote. All organisms other than bacteria are examples of Eukaryote.
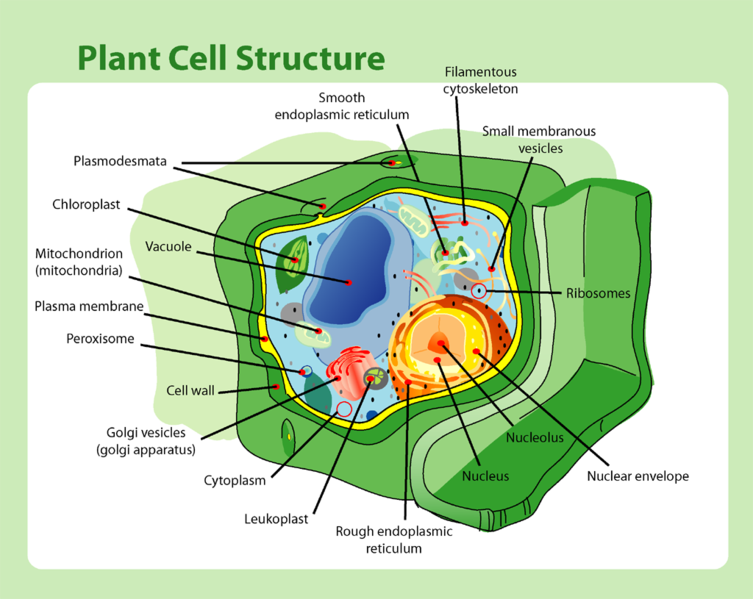
Different parts of a eukaryotic Cell and their functions.
Nucleus: Controls and co-ordinates all the activities of the cell
Mitochondrion: Helps in producing energy from food
Ribosome: Helps in protein synthesis hence, it is called protein factory of the cell.
Centriole: Helps in cell division
Vacuole: Stores wastes, secretions and reserve food products produced in the cells.
Endoplasmic Reticulum: It transports substances from one part of the cell to the other and from one cell to another
Golgi complex: It helps in the secretion of chemicals required for cellular activities
Lysosome: Helps in the digestion of organic substances present in the cell. It destroys its own cell when a cell becomes old or damaged. Hence, it is also called the suicide bag of the cell.
Unicellular organisms.

In such organisms, the single cell feeds, grows, respires, excretes, responds to stimuli and reproduces like any higher or complex organism. Unicellular organisms include Bacteria, certain Algae such as Chlorella, Protozoans such as Amoeba, Euglena, Paramecium, etc.
Multicellular Organisms
There are organisms whose body is made up of many cells. Such organisms are called multicellular organisms.
Various levels of body organization
Organism: Many systems work together in our body to carry out the life processes
Organ System: It is a combination of different organs which work together to carry out a particular function
Organ: It is a combination of different types of tissues which performs a specific function
Tissue: A tissue is a group of cells with similar structure and function.
Cell: It is a tiny basic unit of an organism.
Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| Primitive or incipient, without a nuclear membrane | True nucleus with a definite nuclear membrane |
| Represented by naked DNA | Organized into definite chromosomes |
| Absent | Present |
| Small | Large |
EXERCISES
Four alternatives are given under each complete/ incomplete statement. Choose the correct answer and put a tick (√) mark against it.
1. Micro organisms are invented by
a) Leeuwenhoek b) Parashara
c) Robert Hooke d) Robert Brown
Answer: Leeuwenhoek
2. Cell is discovered by
a) Leeuwenhoek b) Robert Brown
c) Robert Hooke d) Parashara
Answer: Robert Hooke
3. A true nucleus is present in
a) prokaryotic cell b) bacterial cell
c) Virus d) eukaryotic cell
Answer : eukaryotic cell
4. The power house of a cell is
a) nucleus b) ribosome
c) mitochondrion d) lysosome
Answer mitochondrion
5. A group of cells with similar structure and function is a
a) tissue b) organ
c) organ system d) organism
Answer Tissue
II. Fill in the blanks with Suitable Words
1. The combination of different organs which carry out a particular function is called organ system
2. Ribosome helps in protein synthesis
3. Lysosome helps in the digestion of organic substances
4. Paramecium is an example for Unicellular organisms
5. The part which controls and co-ordinates all the activities of the cell is nucleus
6. In a prokaryote, genetic material is represented by Deoxy Ribo Nucleic Acid (DNA).
III. Answer the following questions.
1.Define a cell. Explain the structure of a typical cell.
Cell: A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of an organism.
2.Draw a neat diagram of a eukaryotic cell and label its parts
3.Differentiate between an organ and a tissue.
| ORGAN | TISSUE |
| A group of cells working together is defined as a tissue. | several tissues working together comprise an organ. |
| He tissues perform simpler tasks. | he organs perform the complex functions of the body. |
| The size of an organ is larger than the tissues | The size is smaller than organ. |
4.Mention the functions of the parts of a eukaryotic cell
- Nucleus: Controls and co-ordinates all the activities of the cell
- Mitochondrion: Helps in producing energy from food
- Ribosome: Helps in protein synthesis hence, it is called protein factory of the cell.
- Centriole: Helps in cell division
- Vacuole: Stores wastes, secretions and reserve food products produced in the cells.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: It transports substances from one part of the cell to the other and from one cell to another
- Golgi complex: It helps in the secretion of chemicals required for cellular activities
- Lysosome: Helps in the digestion of organic substances present in the cell. It destroys its own cell when a cell becomes old or damaged. Hence, it is also called the suicide bag of the cell.
5.Distinguish between the following pairs
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| Primitive or incipient, without a nuclear membrane | True nucleus with a definite nuclear membrane |
| Represented by naked DNA | Organized into definite chromosomes |
| Absent | Present |
| Small | Large |
b) Unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Unicellular organisms:In such organisms, the single cell feeds, grows, respires, excretes, responds to stimuli and reproduces like any higher or complex organism. Unicellular organisms include Bacteria, certain Algae such as Chlorella, Protozoans such as Amoeba, Euglena, Paramecium, etc.
Multicellular Organisms: There are organisms whose body is made up of many cells. Such organisms are called multicellular organisms.
6.Draw a neat labelled diagram of a prokaryotic cell.
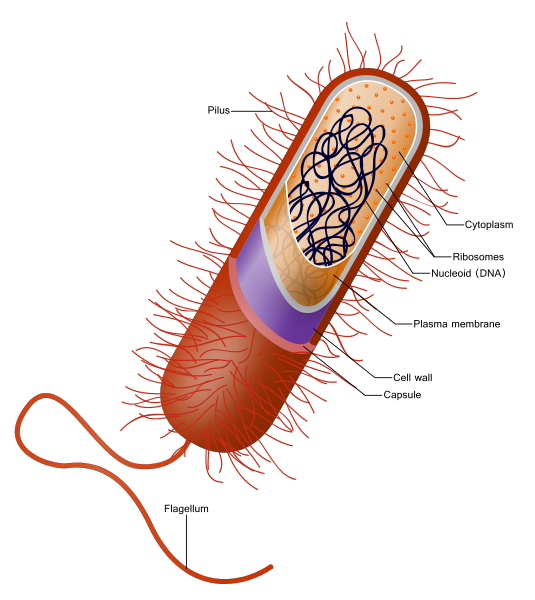
7.Describe the structure of a eukaryotic cell.
The eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes.eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus, numerous membrane-bound organelles (including the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria)several rod-shaped chromosomes.He nucleus is the most prominent organelle in a cell. Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus, which means the cell’s DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Therefore, the nucleus houses the cell’s DNA and directs the synthesis of proteins and ribosomes, The nuclear envelope is a double-membrane structure that constitutes the outermost portion of the nucleus.hromosomes are structures within the nucleus that are made up of DNA, the genetic material. In prokaryotes, DNA is organized into a single circular chromosome. In eukaryotes, chromosomes are linear structures.
8.Name the four levels of body organization in organisms.
- Cells,
- Tissues,
- Organs,
- Organ systems.
9.Mention the advantage of the tissue-organ level of body
organization.
- The main advantage for an organism to have tissue level organization is the division of labour.
- The cells with similar structure and function form tissue to perform a specific activity.
- Different organs form systems like the circulatory system, respiratory system etc.
- Systems carry out separate functions independently and simultaneously. Thus when the lung is purifying the blood, circulatory system is distributing blood throughout the body.
- Single cell type cannot carry out complex functions of organs efficiently.