Sources

Summary
Human beings had created many facilitates to lead their life since ancient times. If the things used by human beings in the past have remained, then they are called as the sources by historians.The agricultural tools left by the earlier people, forts,coins, inscriptions, arms, temples and other religious buildings are considered as sources to write history.
The materials needed for the writing of history are the primary sources. These sources can be divided into two:
a) Literary sources b) Archaeological sources
a) Literary Sources : There are two types in literary sources :
1) Written Literature 2) Oral Literature
Written literature is the main source of literary sources. Literature can bring the contemporary social life of the times of the writer alive to us. A literary work portrays the then existing aspects of life either directly or indirectly. There are two types in written literary forms. They are native Literature and Foreign literature.
Native Literature:The literature created by Indians in native languages is called as the Native Literature. Literary works in Sanskrit, Prakruth, Kannada, Telugu, Tamil, Hindi, Marathi, Kashmiri, Gujarathi, Oriya and in many others native languages are the
sources.These works portray then contemporary social, religious, economic, cultural and political life of people. Kautilya’s ‘Arthashastra’, King Hala’s “Gathaspathasathi’,
Vishaka Dutta’s ‘Mudrarakshas’, Kalhana’s ‘Rajatarangini’, Banabhatta’s ‘Harsha Charitha’, Chand Bhardayi’s ‘Prithiviraja Raso’, Pampa’s ‘Vikramarjunavijaya’, sangam literature, and many other such literary works can be named as native literature.
Foreign Literature:Many foreigners who visited India as travellers, ambassadors, businessmen, officials and missionaries have recorded their observations and experiences in their works. These works are considered as foreign literature. Megasthanese’s ‘Indica’, Fa-hien’s Gho-ko-ki’, Hiuen Tsang’s ‘Si-yu-ki’, Tolemy’s ‘Geography’.Foreign literature, due to lack of local knowledge, many misgivings are recorded. These are the drawbacks of written literary sources. Historians have the challenge of writing history keeping in mind all these limitations.
2.Oral Literature
Oral literature means the folk story, folk songs, folk legends, ballads, and others that pass on from one person to another by word of mouth.The folk people have created ballads about their local heroes. There are ballads on Kumararama, the Nayakas of Chitradurga, Kempegowda, Tippu Sultan etc.There are legends behind the names and places like
Shravanbelagola, Bengaluru, Koppala, Patadakallu, Gokarna and Mysuru.
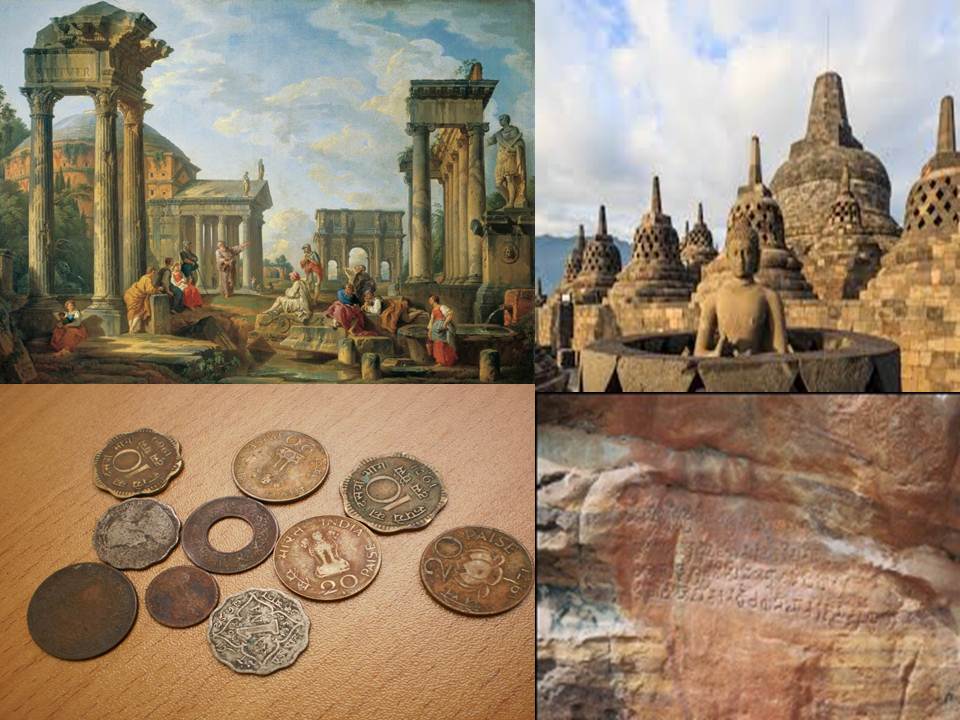
Archaeological Sources

Archaeological sources are divided into four types :
- Inscriptions. 2. Coins. 3. Monuments. 4. Other ruins
Archaeological sources are available not only on the surface of the earth but also hidden deep in the depths of the Earth. The hidden things in the earth are dug out by using scientific methods. This process is called as excavation. During excavation, ruins of buildings, inscriptions, coins, terracotta pieces, bangles, seals, beads, bone pieces, metal and others have been found. These are analysed by applying various scientific
methods to understand the life of people of those times.
Inscriptions

Inscriptions mean engraved writing. Inscriptions are written on stone, rock,
metal, ivory, terracotta and other materials that last longer. Inscriptions are more reliable as these have a direct relationship with then events. Ashoka’s inscriptions are the
earliest inscriptions found in India.
Coins
Coins are small in shape, they contain many important aspects. They are helpful in understanding the geographical extent of the ruler’s kingdom who minted
the coins. They also aid us in knowing the language of administration, titles that the kings
possessed their religion, economic conditions of the times and metal technology in vogue of the particular kingdoms. Samudra Gupta had minted seven different types of gold coins. The availability of Roman coins in Bengaluru proves the fact that this region had trade link with Romans two thousand years back.
Monuments :
Monuments are the major sources to write history. Palaces, temples, forts and pillars etc,. are the monuments only. Aihole and Patadakallu explain the evolution of Indian temple architecture. The monuments of Nalanda and the architecture of Madrasas built by
Gawan in Bidar narrate the importance given to education during those times. The fort of Srirangapatana explains the accomplishments in the area of defence technology.
The monuments throw light on then contemporary religious aspects, technology, economic growth, scientific knowledge and creativity achieved.
Other Ruins

Based on the various pieces of terracotta, bangles,beads and seal procured during the examination, one can understand the socio cultural, economic, political and religious life of then people.Not only this, one can also understand the food habits and pattern of
business of those times. In the excavations conducted at Arikamedu and Patanam in Tamilnadu a large number of evidences were found that speak of commercial contact between South India and Romans. Like this, the remains found at excavations tell many things.
Exercises
I. Answer the following after a discussion with your classmates:
1.How do historians write history?
Ans:The things used by human beings in the past have remained, then they are called as the sources by historians.
2.What is the meaning of source? How many types are there?
Ans:The agricultural tools left by the earlier people, forts,coins, inscriptions, arms, temples and other religious buildings are considered as sources.These sources can be divided into two:a) Literary sources b) Archaeological sources
3.Name any two native literary works.
Ans: Kautilya’s ‘Arthashastra’, King Hala’s “Gathaspathasathi’,
Vishaka Dutta’s ‘Mudrarakshas’, Kalhana’s ‘Rajatarangini’ are some of native literary works.
4.Name any two foreign writers.
Ans: Megasthanese’s ‘Indica’, Fa-hien’s Gho-ko-ki’, Hiuen Tsang’s ‘Si-yu-ki’, Tolemy’s.
5.What is the source which has more reliability for writing history?
Ans:Inscriptions are more reliable as these have a direct relationship with then events.
6.Explain the importance of coins in the writing of history
Ans:Coins are small in shape, they contain many important aspects. They are helpful in understanding the geographical extent of the ruler’s kingdom who minted
the coins. They also aid us in knowing the language of administration, titles that the kings
possessed their religion, economic conditions of the times and metal technology in vogue of the particular kingdoms. Samudra Gupta had minted seven different types of gold coins. The availability of Roman coins in Bengaluru proves the fact that this region had trade link with Romans two thousand years back.
7.What are the aspects on which monuments throw more light?
Ans:The monuments throw light on then contemporary religious aspects, technology, economic growth, scientific knowledge and creativity achieved.
8.By what method, the age of biological fossils can be decided?
Ans:By applying carbon 14 dating procedure on the biological ruins found on these sites one can arrive at the accurate period of the ruins.